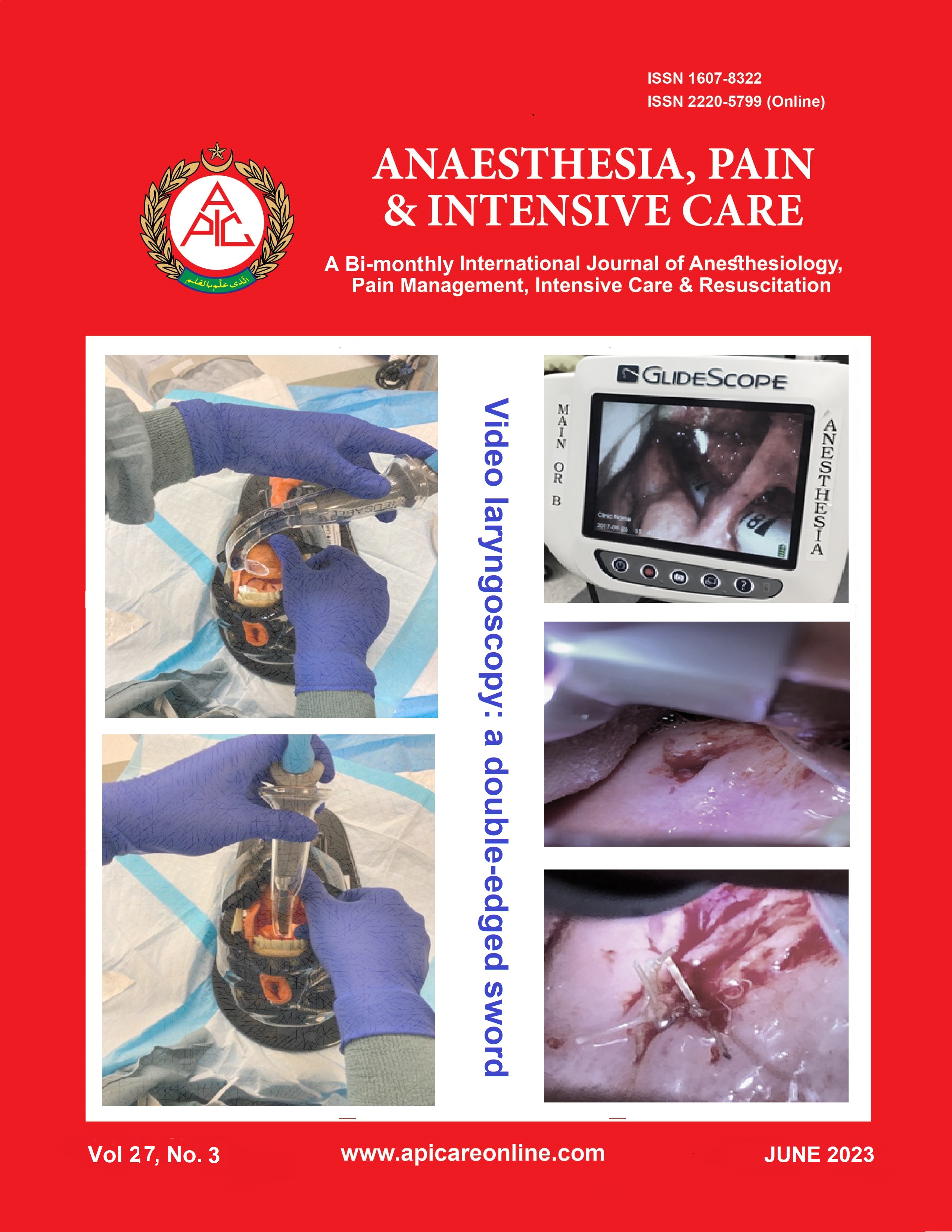
Factors associated with parental self-medication for common childhood illnesses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single centre study
Abstract
Background & Objective: People's interest regarding self-medication increased during the first half of 2020, when the COVID-19 was proclaimed a pandemic, although it has always persisted due to multiple factors. We aimed to identify the factors associated with the use of parental self-medication for their child’s illness during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methodology: A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted at the pediatrics department at Darul Sehat Hospital, Karachi. An interviewer-administered questionnaire was used. We included 275 parents visiting the outpatient clinics with their children of ages 1 to 12 y. Chi-square test of independence was used to check the association of self-medication with studied factors. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Results: Out of 275 parents, 85% were practicing self-medication. 60.3% children suffered from some illness. Parents sought medical advice from pharmacists in 65% of cases, and allopathic drugs were preferred in 64% of cases. 70% of the patients used medicine until recovered, while 41.9% had to seek medical advice. Frequent symptoms obsereved and treated with self-medication were headaches 19.2% and fever 18.8%.
Conclusion: Parental self-medication for common childhood illnesses was substantially more prevalent during the COVID-19 pandemic. Allopathic medicines were preferred choice of parents while pharmacists were commonly consulted for information regarding drugs.
Abbreviations: OTC: Over-the-counter;
Key words: Self-medication; Side effects; Pharmacists: Medications; Antipyretics
Citation: Saeed F, Bham SQ, Mohammed Iqbal M, Sharif UHA. Factors associated with parental self-medication for common childhood illnesses during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single centre study. Anaesth. pain intensive care 2023;27(3):405−412.
Received: December 26, 2022; Reviewed: January 15, 2023; Accepted: April 13, 2023