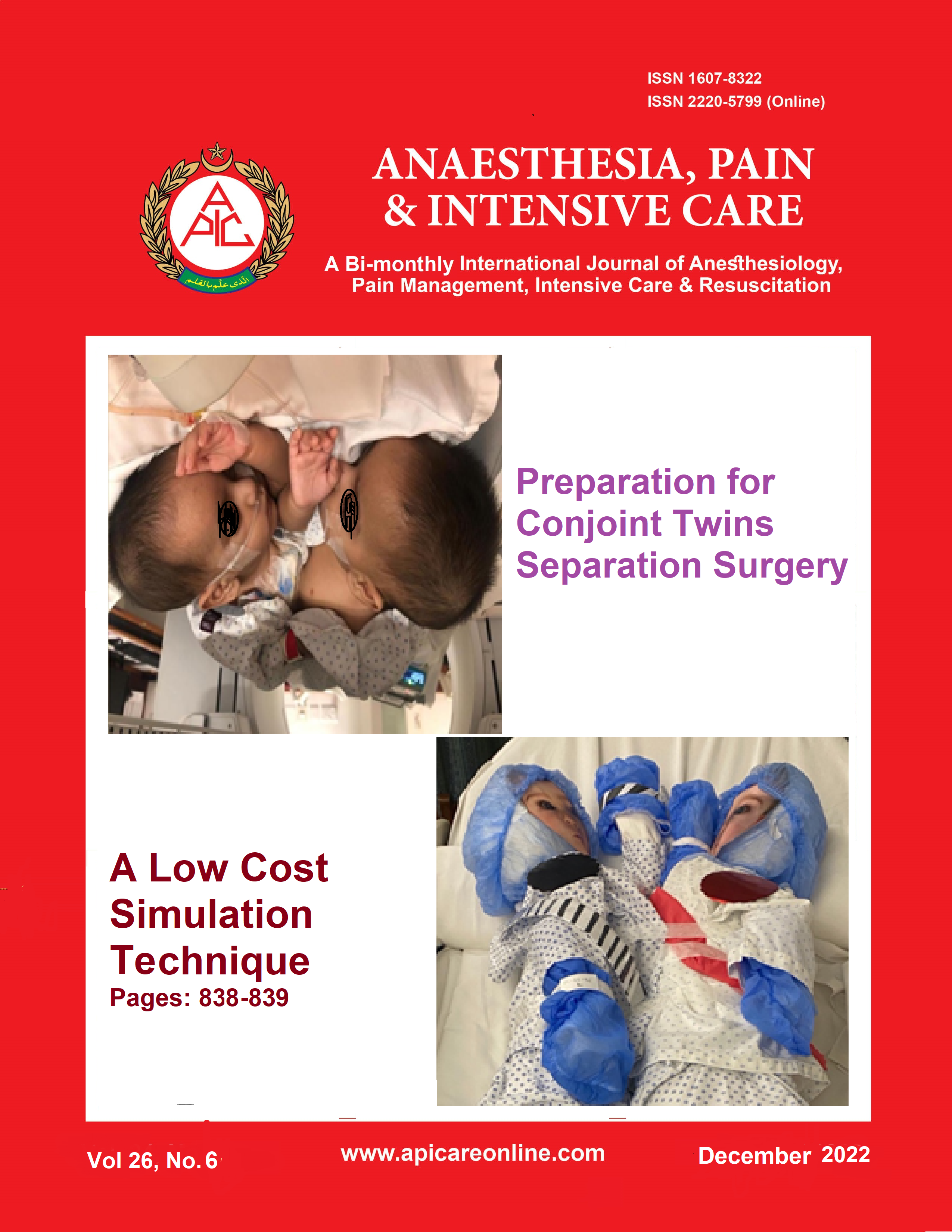
Perfusion index, intraocular pressure, and hemodynamic responses on insertion of endotracheal tube, Air-Q® and Ambu® Aura-I™ in ophthalmic surgeries: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Backgroundː Different supraglottic devices have been used with general anesthesia to avoid the disadvantages of endotracheal intubation (ET), especially the pressor response. We assessed the safety and efficacy of the air-Q® (AQ) and Ambu® Aura-i™ (AI) devices compared to ET during ophthalmic operations under general anesthesia.
Methodology: This randomized clinical trial enrolled 96 adult patients undergoing elective ophthalmic surgeries who were allocated into three groups: the AQ, AI, and ET, according to the airway device used. The perfusion index, blood pressure, heart rate, and intraocular pressure (IOP) were measured before and after the airway device was inserted. The primary outcome was the change in perfusion index, whereas the secondary outcomes included the ease of insertion and changes in the hemodynamic parameters and IOP.
Resultsː Following the insertion of airway devices, the perfusion index decreased significantly in the ET group compared to the AQ and AI groups (P < 0.001). Significant increases in the heart rate, blood pressure, and IOP were observed in the ET group relative to the other groups (P < 0.001). The IOP following insertion of AI was significantly lower than AQ in the first two minutes post-insertion (P < 0.001). The AI device was significantly easier to be inserted than the AQ device (P < 0.001).
Conclusionː Both AI and AQ were reliable and effective in avoiding pressor stress response and increased IOP during general anesthesia, which are desirable targets during operative procedures, especially ophthalmic surgeries. The AI was superior to AQ in terms of IOP fluctuations and the ease of insertion.
Abbreviations: AI: Ambu Aura-i; AQ: air-Q; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; ET: endotracheal intubation; HR: heart rate; IOP: intraocular pressure; LMA: laryngeal mask airway; OLP: oropharyngeal airway pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure; SD: standard deviation; SAD: supraglottic airway device
Key words: Hemodynamic Monitoring; Intraocular Pressure; Intubation, Intratracheal; Supraglottic Airway DeviceCitation: Naguib NN, Mohamed IA, Helmy NY, Obaya GM, Ahmed HM, Khair TM. Perfusion index, intraocular pressure, and hemodynamic responses to insertion of endotracheal tube, Air-Q® and Ambu® Aura-I™ in ophthalmic surgeries: a randomized controlled trial. Anaesth. pain intensive care 2022;26(6):749−756;